Introduction
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape, companies are under constant pressure to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and respond rapidly to market changes. Operational excellence isn’t achieved solely by lean manufacturing principles—it’s also heavily reliant on digital systems that connect the entire value chain. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have emerged as essential tools that bring coherence to an organization’s workflows.
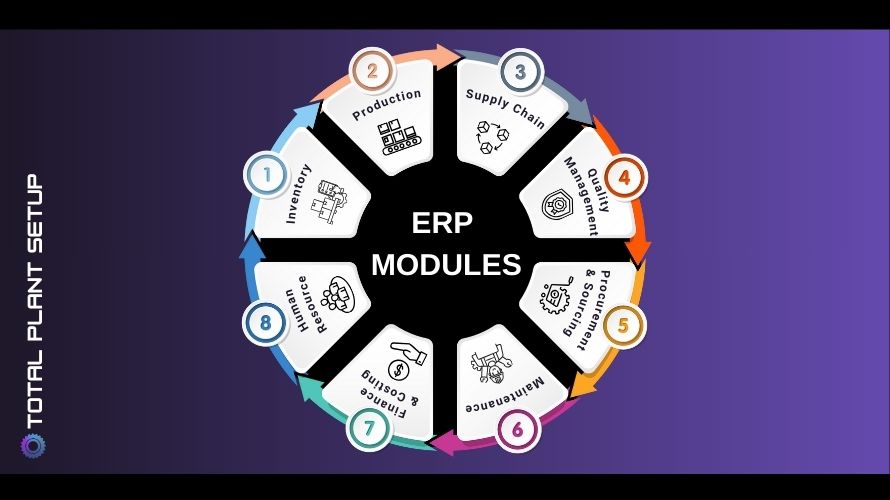
Modern manufacturing systems unify disparate functions, such as inventory, production, procurement, quality, and finance, into a single, integrated software platform. What makes ERP truly powerful are the individual modules that cater to specific operational areas. Choosing the right ERP components, customized for the manufacturing domain, can significantly enhance productivity, compliance, and customer satisfaction. This article explores eight critical system features every manufacturer should implement to gain a competitive edge.
1. Inventory Management Module
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing landscape, companies are under constant pressure to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and respond rapidly to market changes. Functional Units focused on Inventory Management are key to achieving this. Operational excellence isn’t achieved solely by lean manufacturing principles—it’s also heavily reliant on digital ERP modules that connect the entire value chain.
ERP systems unify disparate functions, such as inventory, production, procurement, quality, and finance, into a single, integrated software platform. What makes ERP systems truly powerful are the individual functional units that cater to specific operational areas. Choosing the right Inventory Management modules—customized for the manufacturing domain—can significantly enhance productivity, compliance, and customer satisfaction. This article explores eight critical functional modules every manufacturer should implement to gain a competitive edge. Whether you’re exploring ERP integration for the first time or looking to expand your current system with the best ERP modules for SMEs or large-scale industries, these components are essential for scalable and sustainable growth.
2. Production Planning & Control Module
The Production Planning & Control Module is the backbone of any manufacturing ERP system, responsible for orchestrating how raw materials, labor, and machinery come together to create finished products. Without effective Production Control system features, manufacturers risk machine idling, missed delivery dates, underutilized labor, and production bottlenecks. This module supports the entire lifecycle of manufacturing operations—from generating work orders and managing Bills of Materials (BOMs) to assigning tasks and tracking shop floor performance. At its core, it aligns forecasted demand with available resources, ensuring that production schedules are both achievable and efficient.
Advanced System modules integrate seamlessly with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) for real-time data collection on equipment effectiveness, downtime, cycle time, and operator efficiency. It also empowers production managers with visual tools such as Gantt charts and scenario-based planning to adjust schedules in response to urgent orders or raw material delays. Some solutions even offer AI-driven simulations that help optimize labor distribution and reduce machine idle times. For example, an automotive parts manufacturer using Oracle ERP saw its on-time delivery rate climb from 72% to 90% by linking shop floor feedback directly into its planning system with improved supply chain.
3. Supply Chain Management (SCM) Module
Supply Chain Management (SCM) lies at the heart of manufacturing efficiency, ensuring that materials and components flow seamlessly from suppliers to production lines and, ultimately, to end customers. In today’s globally interconnected manufacturing environment, supply chain disruptions can cripple operations, inflate costs, and lead to missed delivery timelines. The supply chain module within ERP systems offers end-to-end visibility and control over procurement, logistics, vendor collaboration, warehousing, and distribution. Implementing robust quality management systems within ERP frameworks reduces defect rates by 30-45% (ISO 2022 data)
Manufacturers can utilize advanced ERP modules like AI-driven demand forecasting to optimize Inventory Management levels, reduce safety stock, and streamline procurement cycles. With integrated vendor portals and real-time tracking systems, businesses can manage supplier performance, track inbound shipments, and automate replenishment alerts. Features such as drop-shipping support, third-party logistics (3PL) integration, and freight cost allocation further simplify complex operations. These ERP modules also improve customer satisfaction by enhancing delivery accuracy and enabling proactive communication about order status or delays.
Click here to learn more about Supply Chain Optimization & Inventory Management.
4. Quality Management Module
In manufacturing, product quality is directly tied to brand reputation, customer satisfaction, and regulatory compliance. Quality Management Modules (QMMs) embedded in ERP systems serve as the watchdogs of production integrity, ensuring that every item rolling off the line meets established standards. These Functional modules enable manufacturers to implement quality control processes at every stage—from raw material inspection to in-process and final product audits. Modern quality management systems deliver:
- 40-60% faster defect detection (McKinsey 2023)
- 30% reduction in compliance violations
- 25% improvement in audit readiness
QMMs offer automated defect tracking, non-conformance logging, and support for Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA), which are crucial for root-cause analysis and continuous improvement. Many advanced System features now feature IoT sensor integration to trigger alerts when process deviations occur. This real-time feedback loop minimizes the chances of defective products reaching customers and helps ensure consistent compliance with both internal specifications and external regulations.
Explore our Quality & Regulatory Compliance Solutions for deeper insight into regulatory readiness and continuous improvement.
5. Procurement & Sourcing Module
Procurement is more than just purchasing—it’s a strategic process that directly impacts production timelines, cost structures, and product quality. The Procurement & Sourcing Module in ERP systems helps manufacturers efficiently manage vendor relationships, evaluate supplier performance, and ensure timely availability of materials and services. By automating the procure-to-pay cycle, businesses can reduce manual errors, accelerate approvals, and gain greater control over spending.
It also enables multi-tier supplier management, integration with e-auction platforms, and supports sustainability metrics—making it easier to align procurement strategies with ESG goals. With real-time visibility into supplier capacity and compliance status, organizations can better manage supply chain risks and enforce strategic sourcing policies across departments. These ERP components are critical for strengthening the supply chain and improving Inventory Management precision.
6. Maintenance Management Module
In a manufacturing environment, equipment reliability is non-negotiable. When critical machinery breaks down, it not only disrupts production schedules but also drives up repair costs and impacts delivery timelines. This is where the Maintenance Management Module—or Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) module—becomes indispensable. It provides a centralized System module to monitor, track, and manage the entire lifecycle of machinery and plant assets, helping manufacturers shift from reactive to preventive and predictive maintenance models.
The Maintenance module enable intelligent scheduling of maintenance based on usage patterns, service history, and asset criticality. They also help generate audit-ready compliance logs and safety checklists, supporting standards like ISO 55000. Integration with mobile apps allows technicians to receive work orders in real-time and log service details on-site, enhancing the speed and accuracy of repairs. Explore Business Process Automation solutions for digital maintenance workflows and scheduling systems.
7. Finance & Costing Module
Financial visibility is fundamental to effective manufacturing operations, especially in environments where cost pressures and competition are high. The Finance & Costing Module within an ERP system provides manufacturers with the ability to capture, monitor, and analyze financial data in real-time, enabling better decision-making and cost control. This ERP module integrates directly with Procurement, Inventory Management, and Production Control modules to ensure that all financial implications of operational decisions are tracked and reported accurately.
It supports multi-currency operations, handles various costing methodologies such as standard, actual, and activity-based costing, and allows for dynamic budget revisions in response to changing business conditions. The module also includes automated tax compliance, audit trail tracking, and cost variance analysis, helping finance teams identify leakage and drive accountability.
If you’re planning to modernize your financial oversight systems, Please contact us with to get our tailored ERP Implementation Services to scale your business.
8. Human Resource Management (HRM) Module
Manufacturing success is not driven by machines alone—it’s powered by people. From skilled machine operators and process engineers to quality assurance personnel and maintenance technicians, every individual plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth operations. The Human Resource Management (HRM) Module within ERP systems helps organizations manage their workforce more efficiently, aligning human capital with production goals. This ERP module goes far beyond just payroll; it includes workforce planning, time tracking, performance management, training administration, and compliance tracking.
It also integrates with biometric attendance systems, mobile self-service apps, and AI-based recruitment tools, helping HR departments automate routine tasks and focus on strategic initiatives. With shift scheduling synced to production needs and built-in compliance monitoring for labor laws, manufacturers can avoid penalties and improve labor efficiency across departments. This module also tie into Quality Management systems to ensure certifications and training are aligned.
Key Takeaways
ERP Implementation Best Practices Implementing ERP modules isn’t just about installing software—it’s a transformation process. Start with a thorough needs assessment and map your current workflows against desired outcomes. Involve end-users early in the planning phase to gain insights and reduce resistance. Invest in comprehensive training, as even the best ERP modules will fail without adoption. Choose phased implementations when possible to minimize operational disruption and allow for iterative improvement.
Avoid over-customizing modules during deployment, as this can create upgrade challenges and unnecessary complexity. Ensure that legacy data is cleansed and validated before migration. Establish KPIs such as inventory turnover, first-pass yield, or production lead time to track success post-implementation.
ERP Systems Comparison: SAP vs Oracle vs Odoo Feature SAP S/4HANA Oracle ERP Cloud Odoo ERP Ideal For Large Enterprises Large to Mid-sized SMEs & Startups Deployment Cloud & On-Premise Cloud-Only Cloud & On-Premise Strengths Deep industry modules, strong integrations Advanced financials, AI integration Open-source, customizable, cost-effective Weaknesses High cost, complex setup Subscription cost, customization limits Lacks native depth in niche areas Example Use Case Automotive OEMs, Pharma Construction, Retail Local manufacturers, startups.
Common Pitfalls in ERP Implementation
- Inadequate Training – Users may resist adoption if they don’t feel confident using the ERP modules.
- Lack of Change Management – Without strong leadership support and communication, transitions can stall.
- Data Migration Issues – Poor data quality leads to flawed decision-making post go-live.
- No Defined KPIs – Failure to track performance undermines your ability to measure ROI.
- Excessive Customization – Over-tailoring ERP modules makes future updates harder and adds technical debt.
Future Trends in ERP for Manufacturing
- AI-Driven Insights: AI is powering real-time recommendations and predictive maintenance via smart ERP modules.
- Voice-Controlled ERP Interfaces: Especially useful on shop floors where hands-free access boosts productivity.
- Mobile-First Platforms: ERP vendors are developing fully responsive systems for mobile devices.
- Blockchain Traceability: Enhancing trust and authenticity in supplier transactions.
Conclusion
Operational efficiency is no longer optional—it’s a strategic advantage. ERP modules, when implemented thoughtfully, provide the tools manufacturers need to cut waste, increase agility, and compete globally. From inventory control and predictive maintenance to workforce alignment and financial insight, each of the eight ERP modules plays a critical role in building a modern, resilient factory.
Choose your ERP suite and modules based on your unique operational footprint. Whether you’re working with SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics, or an open-source ERP like Odoo, what matters most is how well the ERP modules align with your business goals. When deployed with a solid strategy and the right partners, ERP becomes the foundation of digital transformation in manufacturing.











